
Neurotech - the word itself combines neuroscience and technology. A truly interdisciplinary field, neurotech now sits at the frontier of science, technology, and medicine to deliver new ways to understand, interface, and treat the brain.
Multiple fields combine to deliver multiple perspective into the brain, but what exactly are the applications that neurotechnology uniquely opens?
In this series, we explain the high-level technical overviews of the 10 major types of neurotechnologies today.
This article will cover the first five, check back for the other five technologies.

1. Cognitive assessment & enhancing
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/alzheimers-and-montreal-cognitive-assessment-moca-98617-5bb7c858c9e77c0051582af1.png)
Cognitive assessment and enhancing is a practice designed to help people improve cognitive development, social cognition, and vocational capabilities.
Over the past 30 years, amazing discoveries in neuroscience have opened up the future of cognitive functions. While cognitive function typically declines with age, new neurotechnologies can counteract the effects of aging on brain health and performance.
New research has shown that cognitive function can be assessed and enhanced through a variety of activities, including meditation, video games, smart drugs, nutritional supplements, nutrition, brain stimulation, exercise, music, and cognitive training.
When cognitive function is enhanced, the brain becomes more efficient, allowing us to solve complex problems and understand new perspectives.
Some of the leading companies are Virtuleap, Neurotrack, Mindstrong Health, among others.
 Youtube: Virtuleap | Service introduction video
Youtube: Virtuleap | Service introduction video
2. Neuropharmacology

Neuropharmacology aims to treat neurological diseases and improve patient mood. Hence, it applies to everything from drugs prescribed to help the sick to the recreational "smart drugs".
Neuropharmacology is broadly divided into molecular neuropharmacology and behavioral neuropharmacology.
Molecular neuropharmacology is the study of how drugs affect cellular functions and neural mechanisms with the goal of developing drugs with beneficial neurological effects, while behavioral neuropharmacology is the study of how drugs affect human behavior, including how drug dependence and addiction affect the human brain.
Researchers at pharmaceutical companies, universities, and research hospitals spend more than $137 billion per year to discover new neurotherapeutics, and the pipeline is extremely inefficient, currently taking more than 12 years and $1.5 billion to bring a drug to market. The initial phase of R&D, before clinical trials begin, typically takes 3.5 years.
Some of the leading companies are Sage Therapeutics, AZTherapies, BlackThornx, among others.
3. Neuromodulation
Neuromodulation is "manipulating nerves and neurons through the delivery of artificial stimulus." Examples of this would be to alter neural activity by applying electrical or chemical stimuli to specific nerve sites in the body.
Neuromodulation is a diverse field, with applications ranging from diagnosis and treatment of various diseases to tools for medical and neuroscience research. It also includes pharmacological stimulation with drugs.
Each type of stimulation has different characteristics.
 Neuromodulation stimulation types
Neuromodulation stimulation types
| For Whom | Content | |
|---|---|---|
| Deep Brain Stimulation | Movement disorders such as Parkinson's disease | Electrical stimulation to a specific location in the brain via implanted electrodes |
| Sacral Nerve Stimulation | People with bladder symptoms that don't respond to medication or physical therapy | Changes the function of the sacral nerve near the tailbone. |
| Spinal Cord Stimulation | People with chronic pain | Electrical stimulation with electrodes placed on specific spinal cord regions that may be the cause of pain |
| Vagus Nerve Stimulation | People with depression and epilepsy | Electrical stimulation of the vagus nerve, which is associated with depression and other disorders |
| Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation | People with neurological symptoms such as headaches, and people with psychological symptoms such as depression | Weak electric current generated by the sudden magnetic field change, which excites neurons in the brain. |
According to a market study by NeuroTech Reports, the global neuromodulation market is expected to grow from $8.4 billion in 2018 to $13.3 billion by 2022.
Some of the leading companies are Thync, Axonic, ElectroCore, among others.
 Image: Thync device
Image: Thync device
4. Neuromonitoring / imaging
Neuromonitoring/imaging is a way to scan the brain and spinal cord.
 Neuromonitoring/imaging types
Neuromonitoring/imaging types
Neuroimaging
-
MRI scan
MRI scan, which stands for Magnetic Resonance Imaging, is a test that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the brain and brain stem.
-
PET scan
PET scan, which stands for Positron Emission Tomography, is a tomography scan using a radioactive tracer to examine the brain for disease or damage.
-
CT scan
CT scan, which stands for Computed Tomography, is a type of X-ray examination that produces a three-dimensional image of the head, called a "slice".
Neuromonitoring
-
EEG (ElectroEncephaloGraphy)
EEG can measure the electrical activity occurring in different corticies of the brain. EEG is used to record brain processes that occur immediately after visual or auditory stimulation, but it can also monitor brain states that reflect interaction and motivation over longer periods.
-
MEG (MagnetoEncephaloGraphy)
MEG is a functional nervous technology that maps brain activity by recording the magnetic field produced by naturally occurring electrical currents in the brain using a highly sensitive magnetometer.
While EEG detects the electrical activity produced by neural excitation, MEG captures the magnetic field produced by neural activity; MEG measurements are usually performed in a shielded chamber so that external magnetic fields do not interfere with the data recording.
The biggest advantage is that MEG combines high temporal resolution similar to EEG, but with high spatial resolution.
*Temporal resolution: How short a time interval can be measured.
*Spatial resolution: How well we can distinguish even the smallest objects.
Some of the leading companies are InSightec, NeuroMetrix, among others.
 Youtube: Insightec | introduction video
Youtube: Insightec | introduction video
5. NeuroFeedback
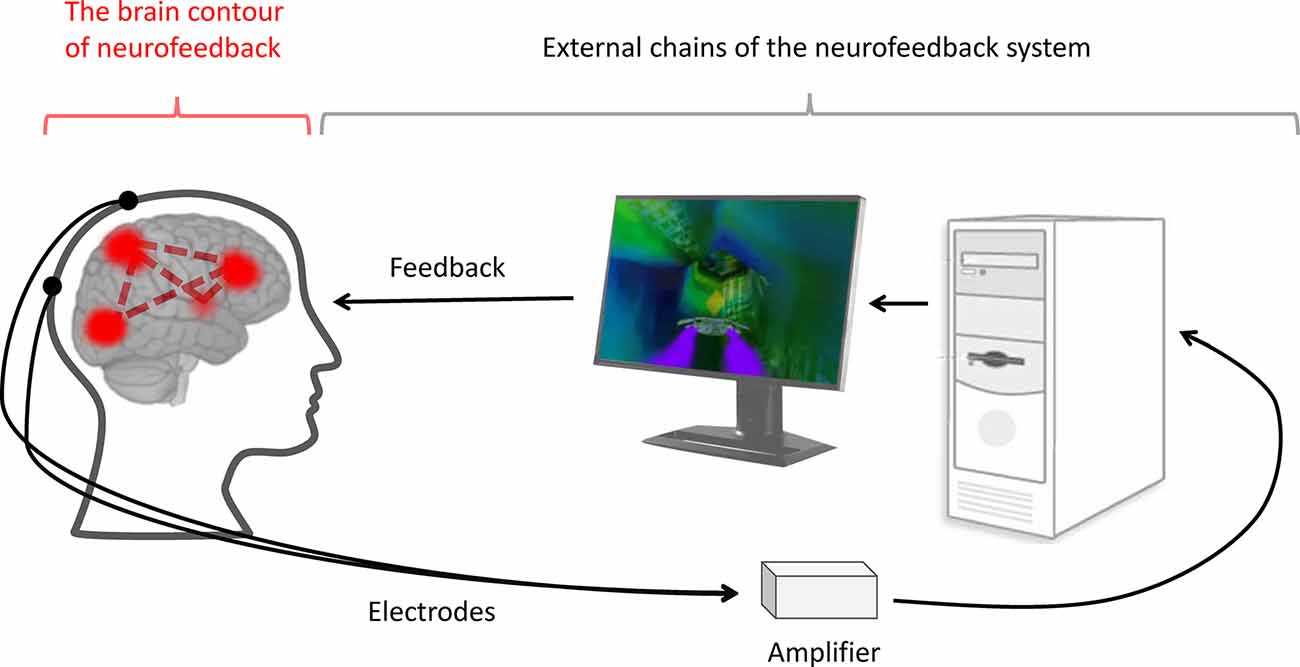 Neurofeedback flow
Neurofeedback flow
Neurofeedback is a technology that visualizes brainwave activity in real-time to understand and train the brain, thereby changing brainwaves and leading to self-regulation of brain functions.
By showing information about the patient's brain wave activity, the patient can learn to change his or her brain waves. Neurofeedback can be used to treat a variety of neurological conditions, such as ADHD, as well as to improve concentration and work productivity.
According to Market Watch reports, the neurofeedback market is projected to be worth $43 million in 2019 and $66 million by 2026.
Some of the leading companies are Muse by InteraXon, Myndlift, BrainCo, among others.
 Image: Muse device
Image: Muse device
In conclusion
In this article, we introduced the first five of the ten technologies that represent Neurotech.
As we have seen, Neurotech is a huge field where technologies from various disciplines such as pharmacy and engineering are applied. There will be more and more startups applying this technology in the future, such as Neuromodulation, which NeurotechJP is especially interested in.
In the next article, we will introduce the latter five technologies.
Data reference:

